Offshore wind-related industries
Offshore wind power involves installing wind turbines at sea, which allows for power generation in areas with better wind conditions compared to onshore locations. Additionally, larger turbines can be installed offshore than on land, enabling the generation of substantial amounts of electricity. For this reason, it is considered a key solution in achieving the primary energy source transition to renewable energy.

Japan, with its large population and limited flat land, faces constraints in locating renewable energy power generation facilities. However, being surrounded by the sea, the country has significant potential for offshore wind power, making it a focal point of attention.
Offshore wind power is highly valued as a critical component in transitioning renewable energy into a primary energy source, and Hokkaido plays a pivotal role in this effort.
Offshore Wind Power: The Key to Making Renewable Energy a Main Power Source
Mass Deployment
- Expansion of adoption worldwide, particularly in Europe
- Rapid growth anticipated in the Asian market
- Japan, surrounded by the sea, is also expected to see increased adoption
Cost Reduction
- In Europe, where offshore wind development is advanced, examples include bid prices falling below 10 yen/kWh and projects operating at market prices (with zero subsidies). Cost reductions are being achieved through measures such as larger turbines.
Economic Ripple Effects
- Offshore wind projects span approximately 30 years, involve numerous components, and have project scales reaching several hundred billion yen.
- While Japan has potential suppliers, the related industries are currently located overseas.
A Major Force Supporting Domestic Installation Targets and Generating Significant Impact
- Implementation Plan
- ●
With five locations in Hokkaido designated as “Promising Areas,” many projects are under consideration to leverage Hokkaido’s favorable wind conditions.
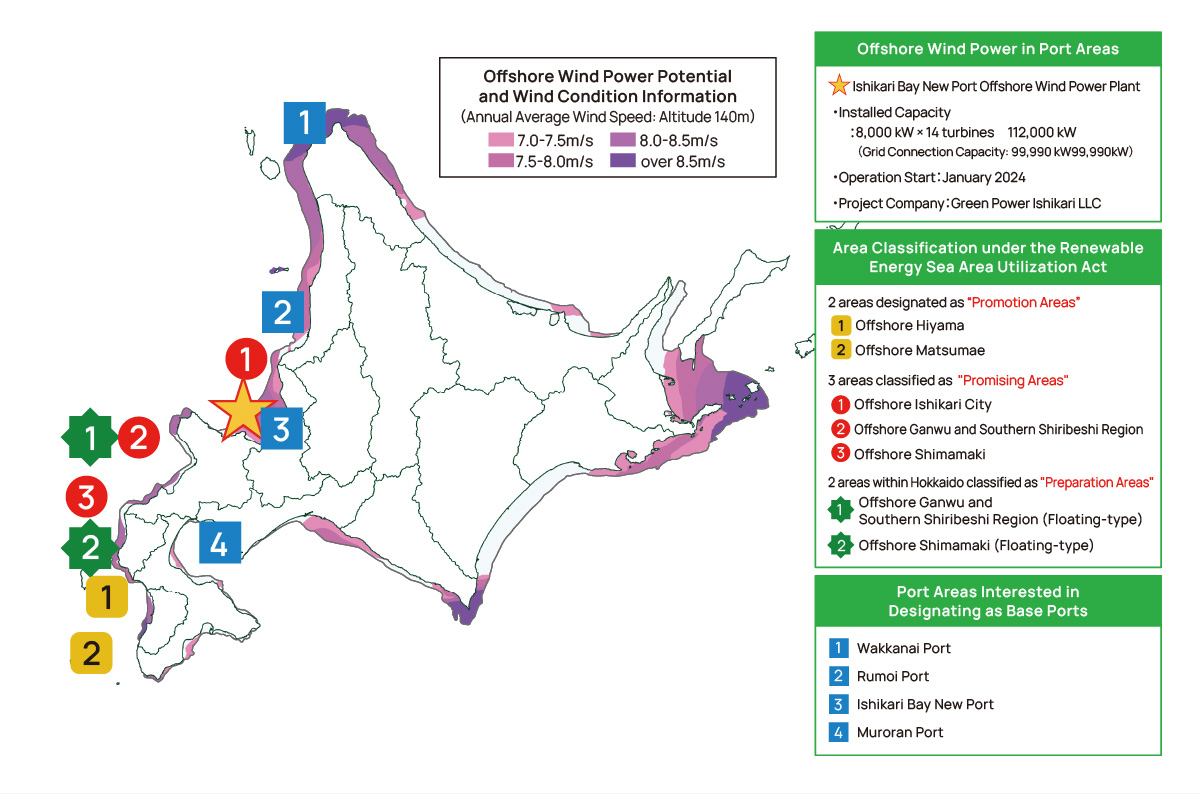
Source: Created based on “Hokkaido’s Renewable Energy Potential and GX Industry Possibilities” by the Hokkaido Zero Carbon Promotion Bureau, Department of Economic Affairs.
- Installation Targets
- ●
The national offshore wind power installation target for 2040 is up to approximately 45 GW. Of this, Hokkaido accounts for about 15 GW, representing one-third of the nationwide target.
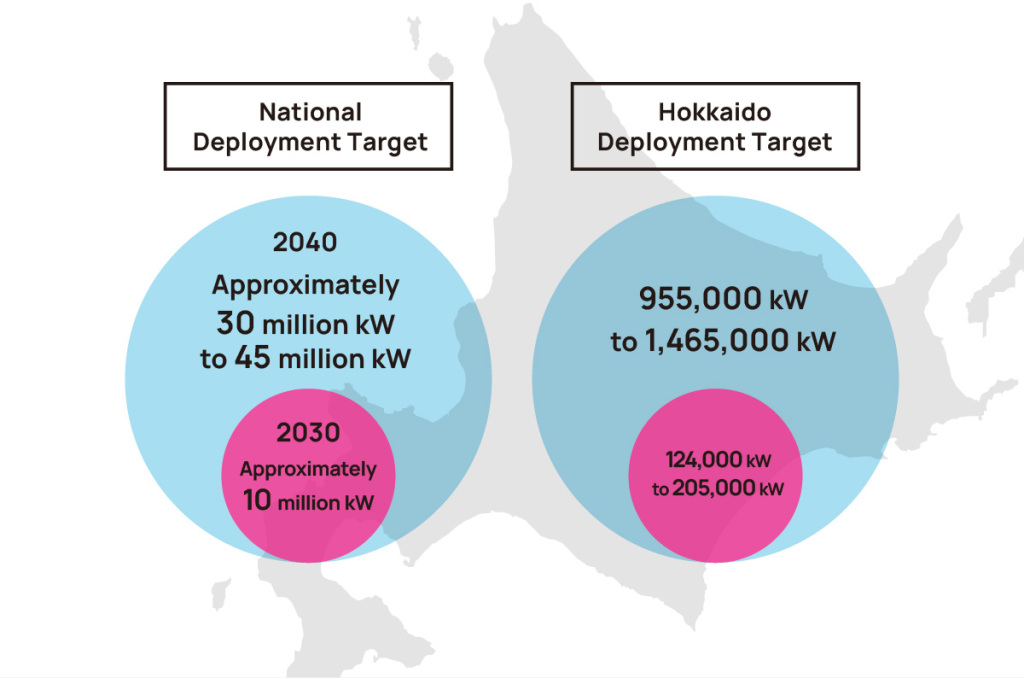
Source: Created based on “Offshore Wind Power Initiatives in Hokkaido” by the Hokkaido Zero Carbon Promotion Bureau, Department of Economic Affairs.
The Impact of Hokkaido’s Installation Targets
Economic Ripple Effects on the Local Economy
- The installation target of 15 GW corresponds to approximately 1,000 wind turbines (*).
- The cost of these 1,000 turbines is estimated at a scale of 3 trillion yen.
[Reference] Japan’s first large-scale commercial offshore wind farms (Akita Port and Noshiro Port) involved 33 turbines with a project cost of 100 billion yen.
(*) Calculation: 14.65 million kW ÷ 15,000 kW per turbine = 976 turbines. This calculation assumes a turbine capacity of 15,000 kW per unit, which is larger than the 8,000 kW per unit capacity of the Ishikari Bay New Port Offshore Wind Farm.
Broad Utilization of Green Power
- The installation target of 15 GW (equivalent to an annual power generation of 45,990 GWh) is approximately 1.5 times the annual electricity demand of Hokkaido (30,078 GWh).
- Utilization in next-generation semiconductor manufacturing hubs and data centers, Conversion into green hydrogen
- Supply-demand adjustments using battery storage systems
- Transmission to areas outside Hokkaido via subsea direct current transmission systems
Efforts to Introduce Offshore Wind Power in Hokkaido’s Port Areas
Introduction of Japan’s Largest Offshore Wind Power and Battery Storage Facility
- Total Output: 112,000 kW
- Grid Connection Capacity: 99,990 kW

















