SAF
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), produced from raw materials such as waste cooking oil and waste products, can reduce CO₂ emissions by 60-80% compared to traditional fuels. The Japanese government has set a target for domestic airlines to replace 10% of their fuel with SAF by 2030. In the future, the use of SAF synthesized from CO₂ and hydrogen is expected to expand further.
Expectations for Synthetic Fuel Produced from CO₂ and Hydrogen
- The Japanese government has allocated a budget for the “Promotion of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) Introduction” project and is considering demonstration projects aimed at building a local production and consumption-based SAF supply chain.
- In the future, the use of SAF synthesized from CO₂ and hydrogen is expected to expand, with the production of SAF also anticipated in regions like Tomakomai through initiatives such as CCUS (Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage).
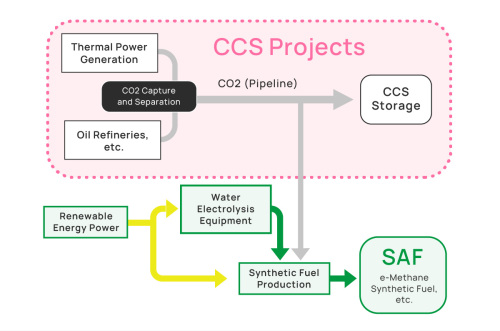
Promotion of CCS (Carbon dioxide Capture and Storage)
- The Japanese government aims to launch CCS (Carbon Capture and Storage) projects by 2030, with a target of storing 6 to 12 million tons of CO₂ annually. To achieve this, the government plans to support advanced and exemplary projects.
- In July 2023, the Tomakomai region in Hokkaido, where JAPEX, Hokkaido Electric Power, and Idemitsu Kosan are advancing studies, was selected for this initiative.
Advanced CCS Support Project [Tomakomai Region CCS Project]
- In the Tomakomai region, a CCUS (Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage) initiative is being promoted, with a focus on integrating CO₂ utilization and recycling (“CCU/Carbon Recycling”) as well as combining biomass power generation with CCS (“BECCS”). The project also envisions the connection of CO₂ transportation pipelines to these systems.
- As part of the carbon recycling initiative, the production of synthetic fuels is being explored using CO₂ separated and captured through the CCS process, hydrogen generated from green hydrogen production, and renewable energy power from Hokkaido as raw materials.